Hymen has some kind of sociological importance at various levels in almost all societies. Especially, in Muslim countries because it is seen as a criteria whether the female has had sexual intercourse before or not, it gains more importance.
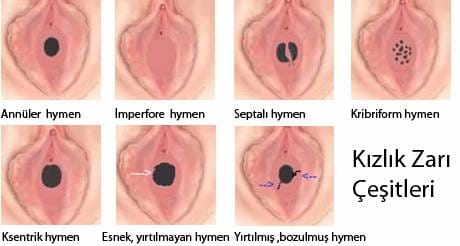
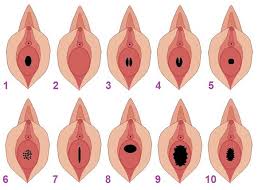
Types of hymen shapes :
Annular hymen (Round circle)
The shape of the hymen is round (circular) and there is a circular hole in the middle. If the hole is large enough, the membrane might not rupture even if the penis passes through. In that case it is said that “the hymen is ready for entry”. The statement elastic membrane is also used. This is the most common hymen shape (60-95%).
Crescentic Hymen
The hymen is shaped like a crescent. While the membrane is thinner or maybe even not present, it is distinct at the back. Frequency of observation is between 3.5% to 20%. These types of hymen do not usually rupture during intercourse.
Septate Hymen
In the middle of the hymen, there is a piece of tissue, which is part of the membrane that divides the emptiness in the membrane. It is seen in 1.5 to 5 % of women.
Cribriform hymen (Lots of punctures)
There is more than one hole in the middle of the hymen. It reminds a sieve. Commonly found in less than 1% of women.
Imperforate hymen (No hole) (Pathologic type)
There is no hole in the middle of the membrane and the vaginal entry is completely closed. Girls with this type of membrane do not have menstrual bleeding. Bleeding occurs regularly however it cannot be discharged and accumulates behind the hymen inside the vagina. It is a painful condition and the hymen needs to be opened through a surgical operation. It is also called as “Hymen Imperforatus”.
Microperforate hymen (Small hole)
The hole in the middle of the hymen is very small. Menstrual bleeding occurs but is very painful. It might require surgical intervention to open.
Carunculae hymen
* In women who give birth naturally (vaginally), the hymen tears and the remaining structure is called a caruncule hymen (remnants of a ruptured hymen).
Your questions…
Can the hymen be seen?
No. It is not really possible to see the hymen for examination because it is 2-3 cm in. Especially, in pregnant women, due to the thickness of the subcutaneous fat, the hymen can be deep inside as much as 4-5 cm.
Does the hymen definitely bleed during the first sexual intercourse?
No. The hymen, although elastic, is an anatomic structure that may tear and bleed easily during the first sexual intercourse. However, specific shapes and structures of the hymen may allow entry of the penis and even though there might be more than one intercourse, it might not tear. These types of membrane are called “ready for entry”. They are also called as elastic hymen. In this type of case, the hymen will only tear after vaginal birth. Additionally, because there are structural differences between people, there might be no bleeding when the hymen is highly elastic or when there are very few veins on the membrane.
Sometimes, it is even possible that there be no veins where the hymen tears or the very tiny ones might clot immediately; thus, no bleeding will be observed. According to one of the main books of medicine, The Merck Manual, in 50% of first sexual intercourse the hymen doesn’t bleed.
Does tearing of the hymen (loss of virginity) cause pain?
Usually, when the hymen tears (virginity loss) there is no pain. However, because some women contract their muscles due to stress or anxiety or in cases when the hymen is thicker – or having higher walls- than normal, pain and bleeding may be more than anticipated. The feeling of pain is also related to a person’s threshold of pain.
Generally, the pain when the hymen tears is not unbearable. The male partner’s attitude and behaviour plays a vital role. The first sexual intercourse is a source of anxiety and fear for every woman. The man’s slow, understanding and gentle approach will provide a smooth, painless intercourse.
Moreover, as it should be done in all sexual intercourses, “foreplay” should be kept as long as possible so that the vagina becomes wet enough and the intercourse will be more comfortable and painless.
How much blood is involved in hymen tears?
The amount of bleeding is usually very little and stops by itself in a short while. However, very rarely, if a vein is dislocated and thus bleeding doesn’t stop surgical intervention and stitching may be necessary. In some cases, tears might happen around the vaginal entrance or even deep inside (coit rupture) and as a result painful and continuous bleeding might be possible. In that case, surgical intervention and stitching will be necessary.
When the hymen tears, does it necessarily bleed?
No. In some instances, even if the hymen is ruptured, there might be no bleeding at all. Especially, if the tear has gone through a veinless area, the person will not have any bleeding.
Does vaginal bleeding indicate tearing of the hymen?
No. Sometimes, the hymen is not ruptured, however, there might be tears or scratches on the outer parts of the hymen and bleeding might be observed in those areas.
Can the hymen break by rubbing?
The hymen doesn’t break only by rubbing. When a material is inserted or when the vagina receives a blow or when the penis enters the vagina, the hymen tears.
Can masturbation damage the hymen?
No. Unless you try to insert something inside the vagina, masturbation doesn’t break the hymen.
How can we understand if the hymen is rupture/broken? How is virginity examination done?
Bleeding (or no bleeding) doesn’t indicate whether the hymen is broken or not. This can only be diagnosed by a hymen examination. It is a very short and painless procedure. The gynaecologist stretches the labia majora (big lips) using gauze strip and observes the hymen. Thus, it can be understood whether the person is a virgin or not.
Virginity examination cannot be done on one’s own. One may be able to see the hymen using a mirror; however, it takes experience to interpret what you see.
Can there be pregnancy without breaking the hymen?
Yes. In order to get pregnant, the hymen doesn’t have to tear. As explained above, with an elastic hymen, although there is complete sexual intercourse and pregnancy, the hymen might not be torn. Another possibility, although rare, is when the male ejaculates too near to the hymen. Since sperms are mobile cells (sperm motility), moving about using their tails, they can enter the vagina through the vaginal entry and from there move to the tubes, reach the egg and start pregnancy (as a result of fertilization) including ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, even if the sexual intercourse is not fully completed, although the chances look slim, the chances of pregnancy (even through ejaculation outside the vagina) are never nil.
Is gynaecological examination or abortion possible without breaking the hymen?
Yes. In cases where the structure or shape of the membrane allows – that is, if the opening is wide enough- , a speculum examination even abortion can be possible without damaging the membrane.
Can a virgin receive gynaecological examination?
One very important phase of gynaecological examination is the “speculum examination” to observe the vagina and the cervix. On regular occasions, the examination of virgins is not done via this method, but through the anus by hand. Moreover, it is possible to take vaginal culture samples from young virgin women and girls who experience vaginal fluid discharge.
Can the hymen be repaired/restored?
Yes. Just by imitating the first intercourse, by restoring the hymen through a surgical operation, it may be possible to have bleeding like in the first intercourse. The restoration of the hymen is called “hymenoplasty”. Surgery to repair the hymen is done to restore it; the reasons are not health related, but they are sociological.